Interactive tip-ins are increasingly vital for enhancing user experience across various digital platforms. From websites and mobile apps to games and e-learning resources, these elements provide crucial context, guidance, and support. This guide delves into the complete process, from designing engaging tip-ins to implementing them effectively and measuring their impact.
This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of creating effective interactive tip-ins, encompassing everything from defining different types of tip-ins to advanced techniques for optimization. We’ll analyze the design considerations, implementation strategies, and testing procedures needed to achieve an exceptional user experience.
Introduction to Interactive Tip-ins

Interactive tip-ins are supplemental information presented in a dynamic manner, enhancing user experience and providing context-sensitive guidance. They are crucial for improving usability and comprehension within a digital interface, guiding users through complex processes or explaining unfamiliar concepts. This approach encourages user engagement and promotes a more intuitive interaction with the system.
Definition of Interactive Tip-ins
Interactive tip-ins are small, contextually relevant elements that appear when a user interacts with a specific part of a design, providing additional information or guidance. They serve as a concise explanation, often using visual cues or brief text, improving user understanding and minimizing the need for extensive documentation. This method of interaction fosters a more engaging user experience.
Purpose and Benefits of Interactive Tip-ins
Interactive tip-ins enhance user comprehension and engagement by providing supplementary information on demand. This targeted delivery of information improves usability, reduces the need for extensive documentation, and allows users to learn and adapt more effectively. They significantly improve the overall user experience by providing immediate assistance.
Types of Interactive Tip-in Elements
Interactive tip-ins can take various forms, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Common types include tooltips, pop-ups, and hotspots. Each type serves a distinct purpose, enabling a diverse range of user interactions and information delivery.
Comparison of Tip-in Types
| Tip-in Type | Description | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tooltips | Small, informative boxes that appear when the user hovers over an element. | Provide concise explanations without interrupting the user flow. Easy to implement and integrate into existing designs. | Can become distracting if used excessively. Limited space for detailed explanations. |
| Pop-ups | Window-based elements that appear when the user clicks or interacts with a specific element. | Can accommodate more detailed information and multimedia content. Good for presenting complex instructions or explanations. | Potentially disruptive to the user flow if not managed carefully. Can be perceived as intrusive. |
| Hotspots | Interactive areas within an image or design that trigger a tip-in when clicked or hovered over. | Provide targeted information directly related to a specific visual element. Effective for highlighting key features or components. | Requires careful planning to avoid cluttering the interface. Can be less intuitive if not clearly marked. |
Designing Interactive Tip-in Experiences
Effective interactive tip-ins go beyond simple annotations. They are carefully crafted to enhance user understanding and engagement, seamlessly integrating into the surrounding content. This involves meticulous planning and design considerations to ensure a positive and productive user experience.Well-designed tip-ins provide concise, valuable information within the flow of the user journey, augmenting the core content without disrupting the main narrative.
By prioritizing clarity, accessibility, and visual appeal, tip-ins become indispensable tools for knowledge delivery.
Key Considerations for Effective Tip-in Design
Thorough planning is crucial for crafting successful tip-ins. Considerations must encompass user needs, platform conventions, and the overall design aesthetic. Understanding the target audience and their learning styles will help to tailor the content to their needs and preferences.
- User-centered Design: Tip-ins should be developed with a deep understanding of the target audience. This includes considering their technical proficiency, prior knowledge of the topic, and preferred learning styles. For instance, users who prefer visual learning might benefit from more imagery and fewer words.
- Platform Consistency: Tip-ins should adhere to the design language and conventions of the platform they reside on. Maintaining a consistent visual style and interaction pattern ensures a cohesive user experience.
- Contextual Relevance: Tip-ins must be seamlessly integrated into the surrounding content. Their placement and design should enhance comprehension and not distract from the main information.
Crafting Engaging and Informative Tip-in Content
The content within a tip-in should be clear, concise, and focused. Complex information should be broken down into manageable chunks, with supporting visuals where appropriate.
- Conciseness and Clarity: Use clear and concise language, avoiding jargon or overly technical terms. Break down complex concepts into smaller, easily digestible pieces. Bullet points and short paragraphs can be extremely helpful in improving readability.
- Visual Appeal: Incorporate relevant images, icons, and diagrams to enhance understanding and engagement. Visual aids can effectively communicate information and break up large blocks of text, making the tip-in more visually appealing and easier to digest.
- Structured Information: Use headings, subheadings, bullet points, and other formatting techniques to structure information logically and improve readability. This improves comprehension and allows users to quickly locate specific details.
Creating a Smooth and Intuitive User Experience
The interaction with a tip-in should be intuitive and straightforward. Users should easily access and dismiss tip-ins without any confusion or frustration.
- Intuitive Interactions: Use clear and simple interaction methods, such as buttons or overlays, for accessing and dismissing tip-ins. Avoid overly complex or confusing controls. For example, a simple click or hover interaction will likely be more intuitive than a complicated animation.
- Accessibility Considerations: Ensure tip-ins are accessible to users with disabilities, following accessibility guidelines. This includes providing alternative text for images, ensuring sufficient color contrast, and avoiding animations that may cause seizures.
- Performance Optimization: Design tip-ins to load quickly and efficiently. Avoid excessive animations or large image files that may slow down the user experience. Optimized loading speeds ensure that users have a smooth and pleasant experience.
Accessibility and Inclusivity in Tip-in Design
Designing for accessibility and inclusivity ensures that tip-ins are usable by a wider range of users, including those with disabilities.
- Color Contrast: Ensure sufficient color contrast between text and background elements to improve readability for users with visual impairments. Guidelines exist to define adequate contrast ratios.
- Alternative Text for Images: Provide alternative text for all images and graphics to improve understanding for screen reader users.
- Keyboard Navigation: Ensure that tip-ins can be navigated and interacted with using only a keyboard. This is crucial for users who rely on keyboard navigation.
Examples of Well-Designed Tip-ins
Well-designed tip-ins are present in various platforms, demonstrating effective integration and user-friendliness. For example, popular productivity apps often utilize tip-ins to introduce new features or functionalities.
- Examples from Popular Platforms: Many popular productivity apps, such as Google Workspace and Microsoft Office applications, often provide interactive tip-ins to introduce new features. These tip-ins are seamlessly integrated into the interface and are easily accessible to users, enhancing their overall productivity.
Examples of Helpful and Visually Appealing Tip-in Content
The content within tip-ins should not only be informative but also visually appealing. Visually engaging tip-ins are more likely to capture and maintain user attention.
- Clear and Concise Information: Effective tip-in content should provide clear and concise information, using simple language and visuals to communicate important points. For instance, a tip-in for a new software feature might provide concise instructions on how to use it.
- Visual Hierarchy: Visual hierarchy can be utilized to highlight key information, drawing the user’s attention to important details.
Implementing Tip-ins in Different Platforms
Tip-ins, as interactive elements, offer a valuable way to enhance user experience across various digital platforms. Effective integration requires careful consideration of the platform’s specific characteristics and user interactions. This section delves into the practical implementation of tip-ins within web pages, mobile applications, and other digital environments.Implementing tip-ins effectively involves understanding how different platforms handle interactive elements and tailoring the approach accordingly.
Careful planning ensures that the tip-ins seamlessly integrate with the existing design and functionality of the platform.
Integrating Tip-ins into Web Pages
Web pages provide a flexible environment for implementing tip-ins, leveraging technologies like JavaScript, CSS, and HTML. These technologies enable dynamic content display and user interaction. Integration often involves creating a container element to hold the tip-in content, and using JavaScript to trigger its display and manage its visibility based on user actions.
Implementing Tip-ins in Mobile Applications
Mobile applications, often with distinct UI frameworks and interaction patterns, require a different approach. Tip-ins might utilize native UI components, custom views, or frameworks like React Native for cross-platform compatibility. The size and layout of tip-ins should be carefully considered for optimal display on various screen sizes.
Tip-in Examples Across Platforms
A common example of a tip-in on a website is a tooltip that appears when a user hovers their mouse over a button, providing a concise explanation of the button’s function. In an e-learning application, tip-ins could guide learners through complex concepts, offering additional context and instructions in a subtle, unobtrusive manner. Games might use tip-ins to display helpful hints or instructions.
Technical Aspects of Implementation
The technical aspects involve selecting the appropriate programming languages and frameworks, creating dynamic elements, and handling user interactions. For instance, in a web application, JavaScript functions can be used to show and hide tip-in content based on user actions. Styling tip-ins using CSS ensures consistent appearance across different browsers.
Coding Examples (JavaScript)
“`javascript// Example of a tip-in triggered by a button click in a web page.const tipInContainer = document.getElementById(“tipIn”);document.getElementById(“myButton”).addEventListener(“click”, () => tipInContainer.style.display = “block”;);document.addEventListener(“click”, (event) => if (!event.target.closest(“#tipIn”) && !event.target.closest(“#myButton”)) tipInContainer.style.display = “none”; );“`
Interactive Behaviors
Tip-ins can incorporate animations and transitions to enhance user engagement. Animations can be used to smoothly reveal the tip-in content, and transitions can control the speed and style of the display changes. Transitions could be subtle fades or more dramatic slide-in effects.
Triggering Tip-ins
Tip-ins can be triggered using different methods. Mouse hover interactions provide a responsive and user-friendly experience, while button clicks offer a controlled method for displaying tip-ins. Choosing the appropriate trigger depends on the context and desired user interaction.
Compatibility Issues
Cross-browser compatibility is crucial for ensuring tip-ins function correctly across different browsers and devices. Thorough testing is essential to address potential discrepancies in rendering and interaction across different platforms. Responsive design principles are also important for adapting tip-ins to varying screen sizes.
Testing and Evaluating Tip-ins
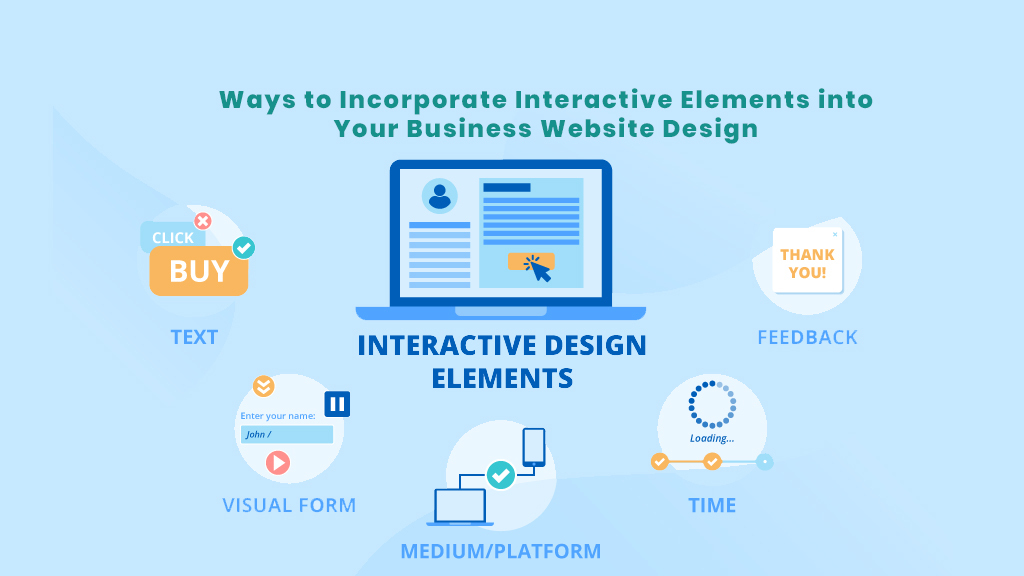
Thorough testing and evaluation are crucial for ensuring interactive tip-ins are effective and user-friendly. A well-designed testing process allows for early identification of usability issues and areas for improvement, ultimately leading to a better user experience. This section details the importance of user testing, methods for gathering feedback, and metrics for measuring effectiveness, all contributing to iterative improvements.
Importance of User Testing
User testing is vital for interactive tip-ins. It allows designers to observe how real users interact with the tip-ins in a natural setting, revealing potential problems and highlighting areas for improvement. This real-world feedback is invaluable for refining the tip-in design and ensuring it meets the needs and expectations of the target audience.
Methods for Gathering User Feedback
Various methods can be used to gather valuable feedback on tip-in design and functionality. These include usability testing, where participants complete tasks while interacting with the tip-ins, and surveys that solicit opinions and preferences. User interviews provide a more in-depth understanding of user experiences and motivations. A combination of these methods is often most effective in comprehensively evaluating the tip-in design.
Metrics for Measuring Effectiveness
Several metrics can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of interactive tip-ins. User engagement, such as the amount of time spent interacting with the tip-in, the number of times it is accessed, and the frequency of interaction, can provide insights into its usefulness. Task completion rates, representing the successful completion of a task with the help of the tip-in, indicate the tip-in’s practical value.
Qualitative feedback, obtained through user interviews and surveys, provides insights into user satisfaction, ease of use, and perceived value of the tip-in. Quantitative data combined with qualitative feedback provides a more complete picture of tip-in effectiveness.
Best Practices for Iterating on Design
Iterative design, based on user feedback, is essential for refining tip-in design. Understanding user behavior and preferences is paramount. Regularly collecting and analyzing feedback from user testing allows for continuous improvements to the tip-in’s design and functionality. This feedback should be used to identify areas for improvement, redesign elements, and refine the tip-in’s presentation.
A/B Testing Process
A/B testing is a valuable method for comparing different versions of interactive tip-ins. Two or more variations of a tip-in are presented to different user groups. Key metrics, like task completion rates and user engagement, are tracked to determine which version performs best. The version with the superior performance is then adopted for wider deployment. Carefully selected metrics and a statistically significant sample size are essential for reliable results.
Potential Usability Problems with Poorly Designed Tip-ins
Poorly designed tip-ins can lead to various usability problems. A tip-in that is intrusive, overly complex, or difficult to understand can hinder user experience. For example, a tip-in that is displayed too frequently or at inappropriate moments can annoy users, decreasing their engagement. Tip-ins that are not contextually relevant or lack clarity can be ineffective, leading to confusion and frustration.
Tip-ins that are poorly formatted or visually unappealing can decrease user interest. These issues, when present, can greatly reduce the effectiveness of interactive tip-ins. Examples include a tip-in that appears unexpectedly during an important task, obscuring critical information, or a tip-in that uses confusing terminology or visual elements.
Advanced Tip-in Techniques
Tip-ins, when implemented effectively, can significantly enhance user engagement and comprehension. Moving beyond basic functionalities, advanced techniques allow for more dynamic and personalized experiences. This section explores sophisticated tip-in interactions, implementation strategies, and optimization methods.Interactive tip-ins are not just static overlays; they are dynamic components that can respond to user actions, adapt to context, and deliver richer learning experiences.
This adaptability is crucial for creating engaging and effective user interfaces. By incorporating advanced techniques, tip-ins can transform from simple supplementary information into valuable interactive learning tools.
Interactive Tutorials
Interactive tip-ins can be structured as mini-tutorials, guiding users through specific procedures or concepts. These tutorials can include step-by-step instructions, visual demonstrations, and interactive exercises, fostering a deeper understanding of the topic. The use of animated sequences, progress bars, and feedback mechanisms can further enhance the user experience. For example, a tip-in demonstrating how to use a new feature could include interactive controls that guide users through the steps, providing instant feedback and ensuring user understanding.
Dynamic Content Updates
Tip-ins can be designed to dynamically update their content based on user actions or contextual information. For instance, a tip-in explaining a specific function could display different content based on the user’s current input or selection. Real-time updates can keep the tip-in relevant and informative, ensuring users have access to the most up-to-date details. This adaptability can improve the overall user experience and efficiency.
For instance, a tip-in on a financial application might update the projected return rate based on the user’s investment choices.
Server-Side Rendering for Complex Tip-ins
For tip-ins with intricate content or dynamic calculations, server-side rendering can enhance performance and scalability. This approach allows the server to generate the tip-in’s content before displaying it to the user, reducing loading times and improving responsiveness, especially for complex visualizations or calculations. This technique is vital for handling large datasets or complex computations, ensuring a seamless and efficient user experience.
For example, a tip-in presenting a detailed analysis of market trends would benefit from server-side rendering to handle the calculations and data aggregation efficiently.
Data Analytics for Optimization
Data analytics plays a critical role in evaluating tip-in effectiveness and identifying areas for improvement. Analyzing user interactions with tip-ins, such as click-through rates, dwell time, and feedback, provides valuable insights into how users perceive and utilize tip-ins. These metrics can be used to refine tip-in design, content, and placement for optimal impact. This approach ensures that the tip-ins are relevant, engaging, and ultimately helpful to the user.
Innovative Tip-in Designs
Recent projects have showcased innovative tip-in designs, incorporating elements like interactive charts, animated sequences, and personalized content. One notable example involves a tip-in that dynamically updates based on the user’s location, providing relevant information tailored to their surroundings. These innovations highlight the potential for tip-ins to be more than just static overlays; they can be interactive and personalized experiences.
Micro-interactions and Animations
Micro-interactions and animations can enhance the user experience within tip-ins, adding subtle cues and feedback. These elements can improve the usability and appeal of tip-ins by making them more engaging and visually appealing. Examples include subtle animations when a user hovers over a specific element or short animations signaling successful completion of a task. Such subtle cues can contribute to a more intuitive and enjoyable user experience.
Adapting to User Needs and Preferences
Tip-ins can be tailored to accommodate individual user needs and preferences. For example, tip-ins can be customized based on the user’s role, experience level, or previous interactions. This personalization ensures that the information presented is relevant and valuable to the specific user. This adaptation is vital to ensuring that tip-ins are truly useful, and not just a distraction.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, crafting interactive tip-ins requires a multi-faceted approach, considering design principles, implementation methods, and rigorous testing. By following the strategies Artikeld in this guide, you can create user-friendly, informative, and engaging elements that significantly improve the overall user experience. Remember that continuous iteration and adaptation based on user feedback are crucial for maximizing the impact of your tip-ins.